Understanding Pyogenic Granuloma: Small Red Spots on the Skin – Causes, Symptoms, and Treatment Explained by Dr. Yeung Ho Hong (楊浩康)
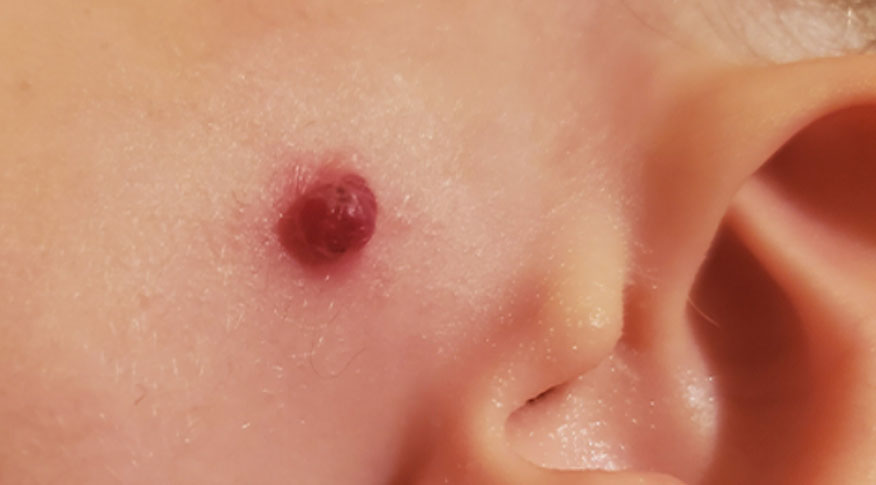
What Is Pyogenic Granuloma?
Pyogenic granuloma is a benign vascular tumor that typically forms on the skin or oral mucosa.
Causes of Pyogenic Granuloma
Pyogenic granuloma is usually caused by local irritation, such as:
- Brushing the gums too hard while brushing teeth
- Localized skin damage
It forms due to tissue proliferation and blood vessel dilation. Additionally, pregnant women are more prone to developing pyogenic granuloma, possibly due to changes in hormone levels during pregnancy.
Symptoms of Pyogenic Granuloma
Pyogenic granuloma typically appears as a red or pink tumor on the skin or oral mucosa, ranging in size from a few millimeters to a few centimeters. It can occur anywhere on the body, but it is most commonly found on:
- Fingers
- Toes
- Oral cavity
- Nose
- Upper lip
This tumor usually develops over weeks or months and tends to bleed easily with minor trauma.
How Is Pyogenic Granuloma Diagnosed?
Typically, a doctor diagnoses pyogenic granuloma by visually examining the tumor’s appearance and reviewing the patient’s medical history. However, a biopsy may be recommended to confirm the diagnosis, which involves removing a sample of the tissue and examining it in a laboratory.
Treatment Options for Pyogenic Granuloma
The primary treatment for pyogenic granuloma is surgical excision. The procedure is usually straightforward and can be performed in a clinic or hospital. After surgery, the doctor may recommend applying an antibiotic ointment to prevent infection. For larger tumors or those in specific locations, alternative treatments such as liquid nitrogen cryotherapy or laser therapy may be suggested.
Summary
Pyogenic granuloma is a common benign tumor typically triggered by local irritation. Its hallmark is the formation of a red or pink lump on the skin or oral mucosa. Diagnosis is generally confirmed through visual inspection and, if needed, a biopsy. Treatment usually involves surgical removal, a simple procedure that can be done in a clinic or hospital. For larger tumors or those in unique locations, doctors may recommend alternative treatments.
